
Have you heard of 404 day? We noticed the wonderful folks over at Internet Archive were celebrating a “new holiday” this Saturday, April 4th 2020, and we thought we would join the party!

If you are fully aware of http status codes, and appreciate the good natured reference to 404 pages, Happy 404 Day! If not – do not fear – a beginners guide to “404” follows.
What does 404 mean?
A “404” is a technical code web developers and website administrators use to describe a page that is shown when a user lands on a page that doesn’t exist on a website. 404 pages tend to be found by accident, often by following a broken link on the web which results in the visitor landing on a page which isn’t there. A link to a page which doesn’t exist is known as a “broken link”.
Many website owners acknowledge that from time to time, their visitors will follow broken links, and therefore configure what are known as “404” pages – 404 pages are shown when the visitor follows a broken link, or types an incorrect URL into a web browser. An example 404 page is shown below.
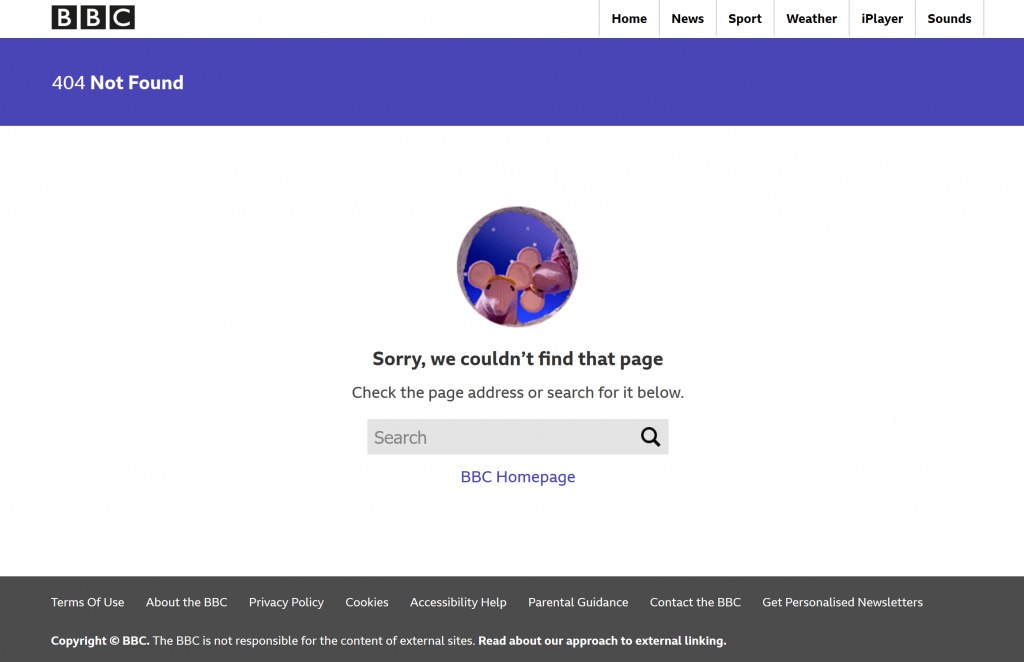
Are 404 pages bad?
While 404 pages are a very normal, everyday experience on the web, they can be very disruptive for a user’s browsing experience. Imagine if you are looking to purchase a gift for a close friend. You browse the web, looking for ideas – maybe checking a review or two. After a little surfing, you stumble across a blogger who seems to be reviewing the perfect gift for your friend!
They have a link to a store that claims to sell the item that will delight them. You are just about to become the planet’s greatest ever buddy by purchasing the perfect, most considerate gift. You click the link.
Imagine the disappointment if you end up not on the purchase page, but instead on a 404 page with no way of purchasing your friend’s dream gift – that’s a bad experience for you, and also a bad experience for the owner of the website who has just lost a sale!
How do 404’s happen?
There are three main ways that 404’s occur:
- A web page gets deleted, breaking links pointing at it
- Someone makes a mistake when they create a link
- Someone goes looking for them deliberately
There is very little worth doing about 404 hunters. Some people are just interested to see what a given site’s 404 page looks like.
Let’s look at the other two causes – where the 404 page is a symptom, rather than cause of a broken link.
How do you fix a broken link?
It’s not just strangers who can accidentally create broken links. Website owners can also sometimes accidentally link to content that isn’t there.
Links on the same site are called internal links. Broken internal links tend to be relatively easy to fix ONCE you’ve found them – they just need correcting.
Links from other sites are called external links, and that’s where things can get a bit more complicated and time consuming. One way of fixing an external link is to try to reach out to the party who made the link and convince them to mend it. Sometimes, that’s straightforward. Sometimes it’s a complicated pain that yields no results regardless of how much effort you put into it.
An alternative route to trying to get other people to fix broken links on their site is to try to change your site to accommodate visitors reaching a 404 page on your site via the broken link. You can either use a “redirect” to bounce the user onto appropriate existing content, or put up new content to replace the 404 page with something meaningful, hopefully improving both the visitors experience and your bottom line!
There is a second, more complicated cause of broken links than mistyped links. This is where content on a website is removed, resulting in any links pointing to the old content becoming broken, and a 404 page being shown.
Website owners therefore need to be careful when deleting content to make sure they consider the impact on site visitors if well-linked-to content is removed.
This issue can lead to website owners trying to save all content so no links will ever break. This strategy is not without danger.
However, if a website owner is scared of deleting content, and wants to preserve it forever – other problems can emerge – like old or stale content presenting visitors with out of date information, promotions or special offers.
Search Engine Optimisation consultants and agencies can help website owners define a content maintenance strategy, which means the most valuable pages are kept up to date, and let you know which pages can be either deleted, or redirected to similar content.
Can I find broken links that result in 404 pages on my site?
Given that a 404 page is a fall-back when a page does not exist which is often the result of a broken link, it can be worth finding and prioritising broken links to your site. There are a number of tools to do this – many of which fall into at least one of the following categories:
- Tools from major search engines
- Log file analysis tools
- Site Crawlers
- Link Maps
One of the most well-known Web Analytics tools for finding 404 pages is the Google Search Console. Google Search Console reports on a number of site problems, including 404 pages, and is considered an essential tool by many website owners.
Log analysis tools can be very powerful. Log files are produced by webservers, and record visitor activity on your website. However, downloading and analysing log files can be complex for the uninitiated, depending on how your website is configured. There are a number of free and paid tools for web file analysis. It’s worth noting that your website hosting provider may include some log file analysis tools as a part of the service.
Site crawlers are programs which download websites to your PC for analysis. Site crawlers can be a great way to find broken internal links on your site. A popular Site Crawler is Screaming Frog – which comes in paid and free versions. The free version is great for smaller sites.
Link Maps – or “backlink indexes” crawl as much of the web as they can, creating a map of how all the pages on the web link together. Link Maps can be very useful for finding out external broken links to your site and others.
Majestic is a Link Map – and features a tool called Site Explorer which can help you find broken links to your site – plans start at just $49.99 US per calendar month.
Find and Fix a broken link on 404 day
We hope you’ve found this guide useful, and challenge you to find and fix a broken link for 404 Day – potentially an easy, cheap way to get – and keep – more visitors on your website.
- Safe Link Building in 2026 - February 19, 2026
- How to Optimize for Google AI Mode - January 23, 2026
- Advanced Filters available across Site Explorer - January 19, 2026







THANKS
April 13, 2020 at 11:20 pm