
What is SEO?
Search Engine Optimisation is a field within Digital Marketing and tends to be performed in conjunction with other promotional and marketing activity. There has been some debate on whether SEO is a role or a function – you can be an SEO or do SEO – the subtlety tends to be if you are performing Optimisation, or being an Optimiser.
Search Engine Optimisation tends to focus on search engine results that aren’t advertisements – this is referred to as “Organic Search”, and due to dominance, Google tends to be the biggest consideration in SEO and we will focus on web SEO. There are, however, other search engines for more specialist content, such as Bing, YouTube, Yandex or Amazon that can be relevant in SEO and are recently receiving more focus.
So what do SEO’s do? This depends on the type of SEO being performed. Depending on who you ask, there will typically be two types of answers to the question, “What are the two types of SEO?” – As we will see, both sets of answers are totally different and totally compatible!
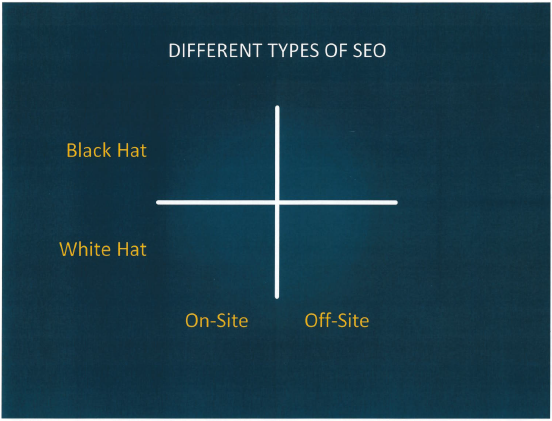
Some people will suggest that the two types of SEO are “Black Hat” and “White Hat”. Others will suggest that the two types are “On-Site” and “Off-Site”. The difference in perspective is really whether you are looking at the split in terms of where SEO’s work, or what guidelines they work.
White Hat/Black Hat refers to guidelines. White Hat SEO’s try to obey the rules of the Search Engine they are considering, and also, to act sustainably. Black Hats tend to be a bit more flexible in their outlook, and tend to try to deliver results regardless of method. Black Hat SEO can be very risky as the Search Engines tend not to like being “gamed”, and can issue “Penalties” – effectively demoting a result – if they expect Shenanigans.
On-site and Off-site are locations of SEO activity. Both cover a range of actions. Whilst, in detail, the boundary can get a little fuzzy, On-Site SEO tends to refer to making your own or your clients’ own site more Search Engine friendly, in the hope that this effort is rewarded by better rankings. Off-site SEO refers to work elsewhere on the internet that attempts to promote the site in question.
At this point, it’s worth noting that Search Engines tend to be quite secretive of exactly how they rank some pages above others in search results. The activities of Search Engines tend to be watched and discussed quite intently by Search Engine Optimisers who produce different models of how Search Engines decide one page is better than the other – so a lot of SEO can be the product of guesswork. Some search engines do produce guidance on SEO or even host forums or tools – such as Googles Webmaster Community, Google Search Console and the Google SEO starter guide. Sticking with the official guidelines tends to see you on the “White Hat” side of the fence.
We also need to have a quick look into how search engines work before we get too far into the nitty-gritty of white hat and black hat link building.
How Search Engines work
Search Engines work in different ways, but a general misconception is that an Internet Search Engine searches the internet – they don’t, as it would take too long to return any search results to the user. Instead, Search Engines can deliver fast results because rather than searching through all the Web Pages or Documents via a relatively slow and unpredictable internet, they search through a simplified copy of these documents, called “An Index” that they hold “in house”.
Because ( as of time of writing 😉 ) no search engine owns the internet, in order to create this local, searchable, ”index”, the search engines use software known as “crawlers” ( crawlers are also known as spiders or bots ) to explore the web and download any content that may be of interest for processing.
Whilst Majestic is quite experienced with web crawlers, a full discussion of Web crawling is way beyond the scope of this document, but for those interested, a couple of relevant starter points are:
- An answer to the question “How Google Search Works” by Google Search Console Help.
- A study of how web crawling works, attributed to a senior program manager at Microsoft.
How does “Crawling” and the process of creating an Index (“Indexing”) impact SEO? Well, On-site SEO is ensuring that the crawler can download the page, and, IF and when the page is downloaded, that the content is relevant and the site conducive to helping the search engine find an appropriate amount of content. Off-site SEO helps in two ways – discovery – helping search engines find documents, and also, quality, relevant links from good websites that are given freely are thought to be a significant ranking factor.
Back to Black Hat and White Hat SEO
So let’s have a look at our 2×2 SEO matrix and break that down into four areas to see the sorts of things Black Hat and White Hat SEO’s get up to both “on” and “off” site – this list is illustrative, and isn’t aimed at any particular search engine. It should be noted that THIS LIST IS NOT A RECOMMENDATION – SOME OF THESE ACTS HAVE SERIOUS CONSEQUENCES.
| White Hat On-site SEO |
• Making sure pages and page content are accessible by search engine web crawlers so the pages can be indexed ( for example by making sure that words in images are repeated in the body of the text which is often easier for computers to understand )
• Creating quality, informative content that helps the reader • Ensuring that content aligns to the sorts of queries that people are asking search engines • Optimising pages to ensure a fast page load speed • Making sure website is cross browser compatable and mobile friendly |
| White Hat Off-site SEO |
• Ensuring that the business is listed in search engine friendly directories like Google Maps
• Conducting a link audit to find any previous “black hat” link building campaigns • Finding quality publications, journalists or influencers as part of a PR based outreach program |
| Black Hat On-site SEO |
• Cloaking – presenting different content to Search Engines than other users
• Stuffing hidden areas of pages with lots of words to try to boost search engine results for this site event though the content does not help the user as they cannot see it. |
| Black Hat Off-site SEO |
• Automatically spamming forums or guest books with Links
• Buying “Follow” links • Using large link exchange or reciprocal link schemes to try to rank pages higher • Using automatically generated content on third party sites to link to a target site |
I’d be hard-pressed to name anyone recommending Black Hat On-site SEO on a client’s site. The reasons are pretty obvious – you are breaking the Search Engine Rules and it’s pretty clear who the guilty party is as the rules have been broken on your site!
A lot of “White Hat” SEO may seem familiar – indeed – since search engines became popular, SEO has become a well-known term, and touches many fields. Website designers are now expected to be reasonably “SEO Savvy” by their clients, and modern PR professionals are also expected to “know digital“.
SEO and Content Marketing, Keywords and Links
By way of expanding on the overlapping nature of White Hat Search Engine Optimisation, we can look at some SEO in action. One way that SEO’s can conduct offsite campaigns is to try to encourage owners of quality, well-ranked material to include links to their site – there are a few approaches to this – including a technique credited to Brian Dean of BackLinko, called the “Skyscraper Technique” – which entails producing best-in-class content and encouraging others to link to it instead of other copy.
This approach of getting quality links from quality publications doesn’t just help search engine results – indeed – any boost in search engine rankings could be thought of as symptomatic of the quality organic referrals such references have.
Commissioning and maintaining high quality, indexable content that is relevant to the audience and accessible by search engines can be a difficult exercise – even for experts – as documented by Olga Mykhoparkina in a report on Search Engine Journal about how they tried to use the “Sky Scraper” technique to build links.
An aspect of the post that is relevant is the use of classic SEO tools to provide digital marketing insights and data.
Difficulties with Organic Search
It’s probably fair to say that most Search Engines are operated as commercial entities, hoping to make a return off of the huge investment it takes to build and maintain a credible web-scale search.
An obvious route to achieving a profit on the loss-leader that is search, is advertisements, and in search, not all search terms are created equal. Some will be far, far more profitable than others, which might cause one to question if a provider of a search engine would seek to balance occasional, complimentary ads in helpful results in interesting niches, with more profitable content where monetisation is easier.
It’s probably fair to say that there is a little bit of a “love-hate” relationship between SEOs and Search Engine providers, and the monetization of search engine results has been somewhat of a hot topic for some time within SEO.
To illustrate where some of the concern lies, try searching for a popular search term – such as “Car Insurance” or “Hotel In London” – our results suggest only two organic searches are returned for “car insurance”, with only google maps results and adverts above the fold for “hotels in London”.
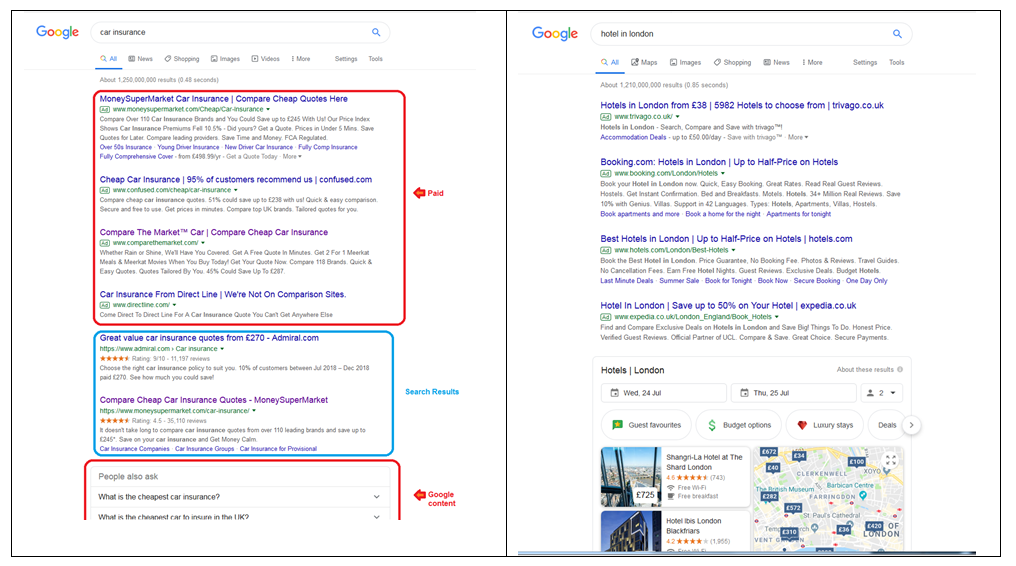
So does this undermine SEO? Not at all – the art of digital marketing has been built on a swamp of fast-moving technology, and change has always been constant.
In the short term, search phrases like “BrightonSEO accommodation” still (at time of writing) yield a high number of organic results – and it is this sort of “Long Tail” results which have been SEO bread and butter for some time – based on more obscure search terms consisting of multiple words, typically having lower volume of search, but often with a higher purchasing intent on the part of the searcher.
Other changes Google have made is the introduction of penalties for link manipulation. These developments have encouraged a White Hat approach to SEO link prospecting which blurs the lines between SEO and Digital PR.
And finally, to finish off with a conclusion…
The more astute reader may notice a range of variations in how some of the terms are represented (“White-Hat” “WhiteHat” “White Hat”). For many years, Search Engine Optimisers would focus on ensuring pages contained many variants of keywords. Whilst Search Engines have got smarter, and the need to vary such wording on pages now tends to be far more succinct, we deliberately chose to leave these terms in by way of rounding out this guide explanation of a common SEO Copywriter Joke – “An SEO Copywriter walks into a Bar… ”.
- Introducing Duplicate Link Detection - August 27, 2021
- Python – A practical introduction - February 25, 2020
- Get a list of pages on your site with links from other sites. - February 7, 2020







I understand the article but would appreciate knowing how to do SEO rather than receiving a rather academic examination of what SEO is – maybe that’s just me though… Will there be any more articles? if so, hoping for more practical bent i’ve just launched a website and I don’t mind spending a little cash, but I do need to place my effort wisely!
July 25, 2019 at 11:35 pmThanks for the feedback – I’ll take that onboard with any future articles!
August 19, 2019 at 7:14 pmTrying to get back into the SEO game – it’s a minefield! I can’t help but wonder if social media and paid ads is now the only logical way forward? Organic seems for too nuanced …
July 29, 2019 at 11:44 amHi Freelance Web Designer, thanks for the comment!
Guessing that your title implies your role, as a freelance web designer it’s likely that you do a lot of onsite SEO like image sizing and naming, are able to optimise page size and download times, and know your way around robots.txt and sitemaps – so I’ll skip the whitehat onsite stuff from this answer and focus on a couple of offsite factors which I hope are worthy of consideration.
There is indeed a lot of cash in paid advertising and unsuprisingly, there are many people offering products or services to make this channel as easy as possible for you. Lots of people have a great deal of success with Paid Ads and Social, and it’s easy to think of these channels as a combined "Silver Bullet".
Paid Ads and Social media can be great outreach tools and fantastic for promoting your site or service – many agencies will use a combination of techniques including paid and organic to try to deliver results for clients – some have the mantra "Paid, Earned, Owned" – a phrase which leads to the suggestion that even if we think of Earned as being limited to Social and Influencer marketing, ignoring SEO can mean you are missing a big piece of the equation in terms of the value of your own content.
To follow on from the article – Well linked to articles can be a great souce of traffic or potential traffic – so knowing which posts on your blog ( for example ) are linked to well can be great intelligence for Web Design and Site maintenance – if you have well linked to content it’s worth preserving in the case of site migrations or structural changes, and maintaining by updating content and ensuring the content remains relevant to users. Whilst Link Building can be a dangerous game – it seems far more white hat to do your bit to maintain the links you have against potential competitor efforts to "steal your leads" by keeping content maintained, relevent and avoiding unecessary 404’s.
Knowing what content you have that is ( or has been ) valuable enough to users and influencers to generate links is important – but so is the insight you can gain from looking at the content your competitors gain links to. From a user experience and market intelligence perspective, there is a lot of gold in knowing who values content enough to link to it, and quite often, a great deal of depth in the opinion expressed in the words of the linking author.
And that’s without considering the Digital PR aspects of Link Intelligence data analysis…
SEO is a big field, but some of it is defensive, and that defensive, intelligence gathering side can be worth considering as a starting point – a link audit to see where you and your competitors gain links from can yield a great deal of benefit, often with relatively little risk.
August 19, 2019 at 7:12 pmFresh, authentic and logical information.
August 12, 2019 at 6:41 amThanks!
August 19, 2019 at 7:13 pmthanks, this very helpfull
August 23, 2019 at 1:58 pmGood stuff guys, thanks.
August 27, 2019 at 1:16 pmI’ve renewed my subscription last month after over a year without it and really glad to see all the improvements on the tool itself and the useful info on your blog.